Harvard engineers are using new resin inks and 3D printing to manufacture new lightweight cellular composite materials.
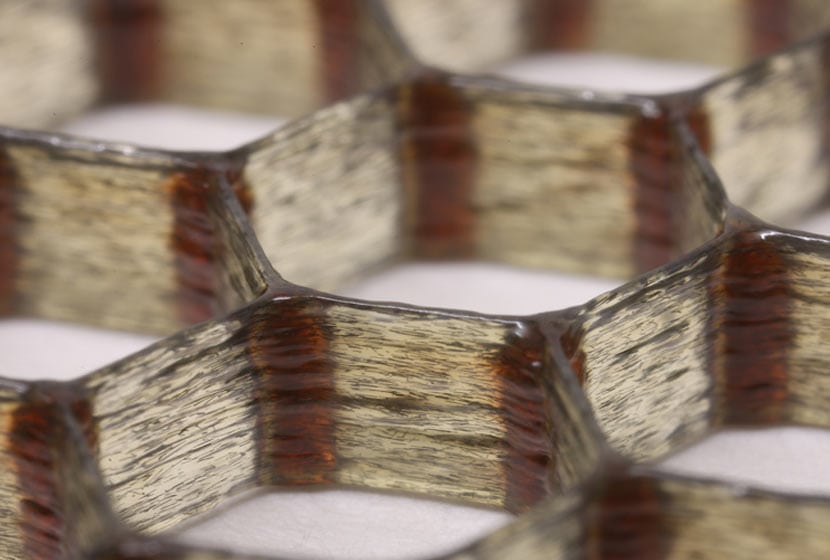
In the world of materials, strength generally goes hand in hand with density. A metal is heavy and solid, a foam is light but with much lower mechanical characteristics. Some counter-examples such as balsa have low density and excellent mechanical properties, thanks to a honeycomb microstructure with a very efficient mixture of cellulose and lignin fibres. Based on this principle, researchers from theHarvard University and Wyss Institute have developed a printed epoxy/carbon honeycomb composite, lighter than balsa, stiffer than concrete, twenty times more efficient than other polymers in 3D printing! As the manufacturing process is digital and automated, the materials can be produced to measure and precisely developed according to specifications.
Until now, 3D printing has been developed with UV-curable plastics and resins. "By using new classes of materials such as epoxy resins, we are opening new avenues for the use of 3D printing to build lightweight architectures".says the researcher Jennifer A. Lewis...professor of bioengineering at Harvard. "This expands the range of materials for 3D printing. »
The result is cellular composites that are stiffer than wood, 10 to 20 times stiffer than commercially available 3D-printed polymers, and twice as strong as printed polymer composites.
Materials specialists at Harvard University have created lightweight cellular composites using 3D printing. These fiber-reinforced epoxy composites mimic the structure and performance of balsa wood. Because the fiber loads aligned along the printing direction, local orientation can be finely controlled, these 3D composites can be useful for wind energy, automotive and aerospace applications, where high strength-to-weight ratios are required.
"As we gain additional levels of control in fill alignment and learn how to better integrate this orientation into component design, we can further optimize component design and improve material efficiency.adds Compton, an additive scientist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. « Finally, we will be able to use 3D printing technology to change the degree of fiber filling alignment and local composition on the fly..
The work could have applications in many areas, particularly in the automotive industry, where increasingly lighter materials are key to achieving the fuel economy standards demanded by the government. One estimate is that one billion cars worldwide could produce $40 billion in annual fuel savings.
3D printing has the potential to radically change manufacturing in other ways. Lewis believes the next step will be to test the use of thermosetting resins to create different types of architectures, particularly by exploiting the filler mixing technique. This could lead to advances not only in structural materials, but also in conductive composites.
Photo Optical photography of a translucent hexagonal honeycomb printed using epoxy ink base with carbon fibres.the aligned black fibres are clearly visible in the cell walls and throughout the structure. The complete structure is 3 mm high and 30 x 40 mm in area, with cells that are 6 mm wall to wall. ( ©Brett G. Compton, Harvard University).
(Source: Harvard School - 2014 - matériO')